Federal funding for research plays a crucial role in driving innovation and economic growth in the United States. As significant cuts to funding loom, the potential impact on the startup ecosystem could be profound, stifling entrepreneurship and innovation that stem from well-resourced research institutions. The ongoing controversy surrounding funding at prestigious institutions like Harvard highlights the ripple effects of such financial decisions on a national scale. The loss of billions in federal grants not only endangers vital research but also threatens to undermine the very foundation of U.S. economic competitiveness. Economists warn that without this crucial support, the nation risks experiencing a damaging downturn, reminiscent of the struggles faced during the Great Recession, with startup ventures facing unprecedented challenges to thrive and sustain creativity.
Government grants for scientific exploration serve as the lifeblood of technological advancements, vital to nurturing groundbreaking ideas within various research sectors. The complex relationship between academia and entrepreneurship underscores how universities can catalyze start-ups through robust research and talent development. At the heart of this dynamic lies a commitment to fostering an environment where innovation flourishes, enabling students and faculty alike to transform theoretical work into practical applications. The interruption of funding threatens not only research projects but also the entire entrepreneurial landscape that relies on these innovations venturing into the market. In summary, sustaining federal financial support is essential to ensure the continued progress and influence of American entrepreneurship on the global stage.
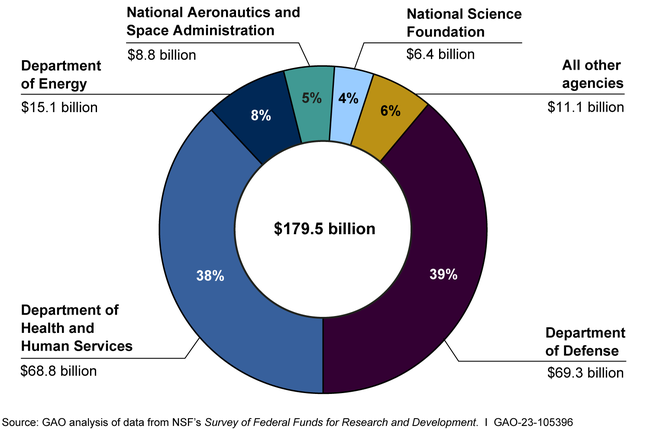
The Critical Role of Federal Funding for Research
Federal funding for research serves as a cornerstone of innovation in the United States, facilitating groundbreaking discoveries that lead to commercial ventures. By providing necessary resources, grants empower researchers to explore unanswered questions, yielding scientific advancements critical to technological and biomedical progress. Without adequate federal support, laboratories risk stagnation, diminishing their capacity to generate novel ideas that can transition into successful startups. Such funding not only nurtures existing projects but also attracts top talent, creating an environment ripe for entrepreneurship.
The economic implications of a decline in federal funding are profound. With reduced financial backing, research institutions face the potential closure of programs, hindering their ability to produce high-impact research. This stunted growth directly affects economic growth; studies have shown that every dollar invested in biomedical research yields exponential economic activity. In scenarios where funding decreases, projections indicate significant drops in GDP, resonating with historical instances from the 2008 recession, which underscores that trends in research funding directly correlate with the health of the broader economy.
Impact of Funding Cuts on Innovation and the Startup Ecosystem
The implications of funding cuts are not confined to the academic sphere but extend deeply into the startup ecosystem. Disruptions in research funding can lead to fewer breakthroughs emerging from universities, subsequently reducing the innovative capacity required for entrepreneurship. Startups, which often rely on findings from academic research to inform their products and services, may find themselves hampered by a lack of accessible knowledge and technological advancements. This cascading effect may thwart budding entrepreneurs who depend on robust research findings to validate their business ideas.
Moreover, funding cuts can cause a chilling effect on the startup community. In an ecosystem where innovation thrives on collaboration between universities and new ventures, any signs of instability can deter investment from venture capitalists. Without the comfort of a vibrant research landscape, investors may hesitate to back new projects, causing a decline in the overall entrepreneurial climate. Essentially, this vicious cycle deprives the economy of growth, as fewer startups translate to fewer job opportunities and reduced economic dynamism.
Long-term Consequences of Research Fund Freeze
The long-term consequences of a federal funding freeze are grave. As highlighted by economists, interruptions in consistent financing lead to delayed projects and potential cancellations of promising research initiatives. The pipeline for innovation is not instantaneous; it often takes several years for lab-based ideas to evolve into commercial products. This timeline indicates that today’s funding turbulence will echo through the economy for years to come, stifling growth and reducing the number of future startups entering the market.
In response to the freeze, research institutions may face difficulties in maintaining their competitive edge. As other countries invest heavily in their science and technology sectors, a stagnation in U.S. funding could lead to a brain drain as top-tier talent seeks opportunities abroad. The implications are twofold: a decrease in groundbreaking research domestically and an economic lag in technological advancement that may cost the U.S. its leadership in various fields.
Consequences of Evolving Entrepreneurship Curricula
Educational programs focusing on entrepreneurship and innovation play a crucial role in creating the next generation of leaders and innovators. Harvard Business School’s approach to integrating entrepreneurship into its curriculum signifies a commitment to fostering an entrepreneurial spirit among students. This intentional design encourages students not only to learn theoretical concepts but also to transform their ideas into viable business models that can thrive in the market.
As the landscape of entrepreneurship evolves, the importance of a well-rounded education that encompasses technology, business acumen, and practical experience becomes ever clearer. Programs that provide hands-on opportunities for students to engage with real-world issues help develop skills crucial for navigating the complexities of launching a startup. These educational initiatives are vital, especially in times of funding constraint, as they equip aspiring entrepreneurs with the knowledge and tools necessary to innovate and contribute to the economy.
The Interconnectedness of Research and Economic Growth
Understanding the interconnectedness of research funding and economic growth is crucial for policymakers. When investment in scientific research is prioritized, the potential for radical innovations that drive economic growth also increases. For instance, biomedical advancements can lead to the development of new treatments and technologies that enhance public health, reduce healthcare costs, and improve productivity across various sectors.
Conversely, economic downturns can lead to a vicious cycle where reduced funding diminishes research output. To maintain the U.S. as a global leader in innovation, it is essential to create policies that not only protect existing funding avenues but also seek new strategies for investment. The relationship between federal funding and the economy underscores the importance of maintaining robust research funding to ensure sustained progress and entrepreneurship within the nation.
Navigating the Challenges of Startup Creation
Navigating the landscape of startup creation in the wake of federal funding cuts involves addressing various challenges entrepreneurs face. The funding environment is crucial to the nascent phases of a startup. Entrepreneurs often rely heavily on grants and venture funding sourced from research outputs. As federal support dwindles, startups find themselves scrambling for alternatives, sometimes resulting in sub-optimal funding scenarios that hinder their growth and innovation.
To counteract these challenges, it is vital for entrepreneurs to forge relationships with venture capitalists who are still willing to back innovative ideas. Additionally, fostering collaborations with research institutions remains critical for accessing cutting-edge research and technological advancements. Developing strategic partnerships can help mitigate the impact of federal funding cuts, ensuring that startups still have the means to innovate and contribute positively to economic growth.
The Vital Incubation Role of Research Universities
Research universities serve as essential incubators for startups, providing a fertile environment for innovation. By offering resources such as access to labs, expert faculty, and networking opportunities, these institutions foster collaboration and engagement among aspiring entrepreneurs. This supportive ecosystem encourages experimentation and the development of ideas into viable business entities. The relationship between research and practical application is critical; it is within university settings that many entrepreneurial ventures find their initial spark.
As these institutions face funding cuts, the startup landscape may radically shift. Research universities equipped with the right resources and connections can dramatically enhance a startup’s chances of success, but with potential funding reductions, those resources could diminish, leading to fewer incubated businesses. Consequently, maintaining a robust investment in research universities is vital to ensuring their continued role in propelling entrepreneurship and fostering innovation.
Understanding the Impact of Economic Recession on Research Funding
Historical trends highlight that economic recessions often lead to cuts in research funding, which poses a direct threat to innovation. During challenging economic times, policymakers may prioritize immediate economic relief measures over long-term investments in research, undermining the foundational support that drives future economic growth. This short-sighted approach can inhibit advancements crucial for emerging sectors and technologies.
Moreover, understanding the cascading effects of reduced research funding during times of recession involves recognizing how quickly innovation can decelerate. When funding is cut, the number of successful research projects may decline, leading to fewer patented technologies and entrepreneurial startups. As the economy slowly recovers, these voids can leave lasting gaps in the market, potentially hindering sustained economic growth and technological leadership for years to come.
Addressing the Future of Research Funding
To address the looming concerns regarding federal funding for research, a multifaceted strategy is necessary. Engaging various stakeholders, including government, academia, and the private sector, is essential for redefining how research is funded and prioritized in national policy discussions. This collaborative effort can identify innovative funding solutions that alleviate dependency on traditional federal sources while simultaneously ensuring a stable environment for scientific exploration and entrepreneurship.
Creating a culture that values research investment as vital to economic well-being is essential. Programs that demonstrate the tangible benefits derived from research funding should be amplified; these include job creation, public health improvements, and advancements in technology that enhance daily life. By fostering public awareness and political will around the importance of research funding, we can better position the U.S. for future success in innovation and economic growth.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the impact of funding cuts on federal funding for research at universities like Harvard?
Cuts to federal funding for research, particularly at institutions like Harvard, pose significant risks to innovation and entrepreneurship. With over $9 billion targeted for review, potential funding losses could shrink GDP by 3.8%, similar to the Great Recession, limiting the capacity for universities to foster breakthroughs that fuel economic growth.
How does federal funding contribute to the startup ecosystem and economic growth?
Federal funding for research is crucial as it enables universities to develop groundbreaking technologies and attract global talent. This funding incites innovation by allowing researchers to create novel ideas, which serve as the foundation for startups, thereby stimulating economic growth through the commercialization of scientific advancements.
Why are research universities critical for entrepreneurship and innovation in the U.S.?
Research universities function as incubators for entrepreneurship and innovation by providing resources and structured programs to support faculty and students. Federal funding for research plays a vital role in maintaining these resources, ensuring researchers can turn their lab discoveries into impactful ventures in the startup ecosystem.
What are the long-term consequences of federal funding cuts for startups and research initiatives?
The long-term consequences of federal funding cuts for research can lead to a slowdown in the creation of startups and the commercialization of research. This can stifle innovation, limit the growth of new companies, and ultimately have adverse effects on economic growth, as fewer innovative solutions enter the market.
How does federal funding for research affect competitiveness in technology and biomedical fields?
Federal funding for research enhances competitiveness in the technology and biomedical fields by enabling universities to invest in state-of-the-art labs and attract top-tier talent. This leads to high-quality research outputs, fostering entrepreneurship and innovation that are essential for maintaining U.S. leadership in these critical sectors.
What role does Harvard play in the relationship between federal funding for research and the startup ecosystem?
Harvard plays a pivotal role in bridging federal funding for research and the startup ecosystem. Its resources, including dedicated labs and an entrepreneurial curriculum, are heavily supported by federal grants, which stimulate innovation and enable students and faculty to launch successful startups that drive economic growth.
Can the damage caused by federal funding freezes be reversed, and how long will it take?
While the damage from federal funding freezes can potentially be reversed, it may take one to three years to fully recover. The timeline reflects the duration necessary for research initiatives to evolve into commercially viable startups, highlighting the critical link between sustained funding and long-term economic development.
What immediate effects do cuts in federal funding for research have on NIH and other grant programs?
Immediate effects of cuts in federal funding for research include hiring freezes, canceled initiatives, and a withdrawal of previously approved grants. These disruptions can undermine the research pipeline, impacting the emergence of new startups and hindering overall economic growth.
| Key Topics | Details |
|---|---|
| Federal Funding Impact | Harvard faced a $2 billion funding freeze due to political demands, affecting research in science and technology. |
| Economic Consequences | Projected GDP shrinkage of 3.8% likened to the 2008 recession; $2.56 generated per $1 invested in biomedical research. |
| Startup Ecosystem | Research universities like Harvard incubate startups through faculty-led innovations and robust entrepreneurship programs. |
| Long-term Effects | Immediate impacts are visible with hiring freezes; expect fewer startups in coming years as funding disrupts the pipeline. |
| Future Outlook | Time required for lab innovations to materialize into companies; reversal of damage is possible, but will take 1-3 years. |
Summary
Federal funding for research is essential to ensure the U.S. maintains its position as a leader in innovation and economic growth. The freeze on funding at institutions like Harvard has already begun to impact research quality and startups, threatening the long-term viability of the entrepreneurial landscape. Investing in scientific research not only fosters academic excellence but also enhances the potential for groundbreaking technological advancements that can lead to significant economic activity. Without adequate federal support, the consequences on both research outcomes and the broader economy could linger for years.