The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that has left many Americans struggling to secure a stable place to live. Over recent decades, skyrocketing home prices and stagnating wages have widened the gap between income levels and housing costs, making homeownership seem like a distant dream for millions. This crisis is exacerbated by stringent land-use regulations and pervasive NIMBY policies, which often stifle the potential growth of the housing market. As the construction industry grapples with these obstacles, productivity has dwindled, resulting in fewer homes being built to meet the rising demand. Without significant policy changes aimed at improving construction productivity and altering land-use practices, the path to affordable housing remains bleak for future generations.
The ongoing dilemma surrounding accessible housing options continues to unfold throughout urban and suburban landscapes, where costs have become increasingly unmanageable. This predicament — often referred to as the housing affordability challenge — reflects a convergence of economic and socio-political factors, including restrictive land planning and community opposition to new developments. Such hurdles, combined with diminishing innovation in building techniques, have led to stagnation in the home construction sector. Consequently, the dream of homeownership is fading for many families, as housing prices escalate without corresponding wage growth. Addressing these intricate issues is essential for revitalizing not only the housing market but also the broader economy.
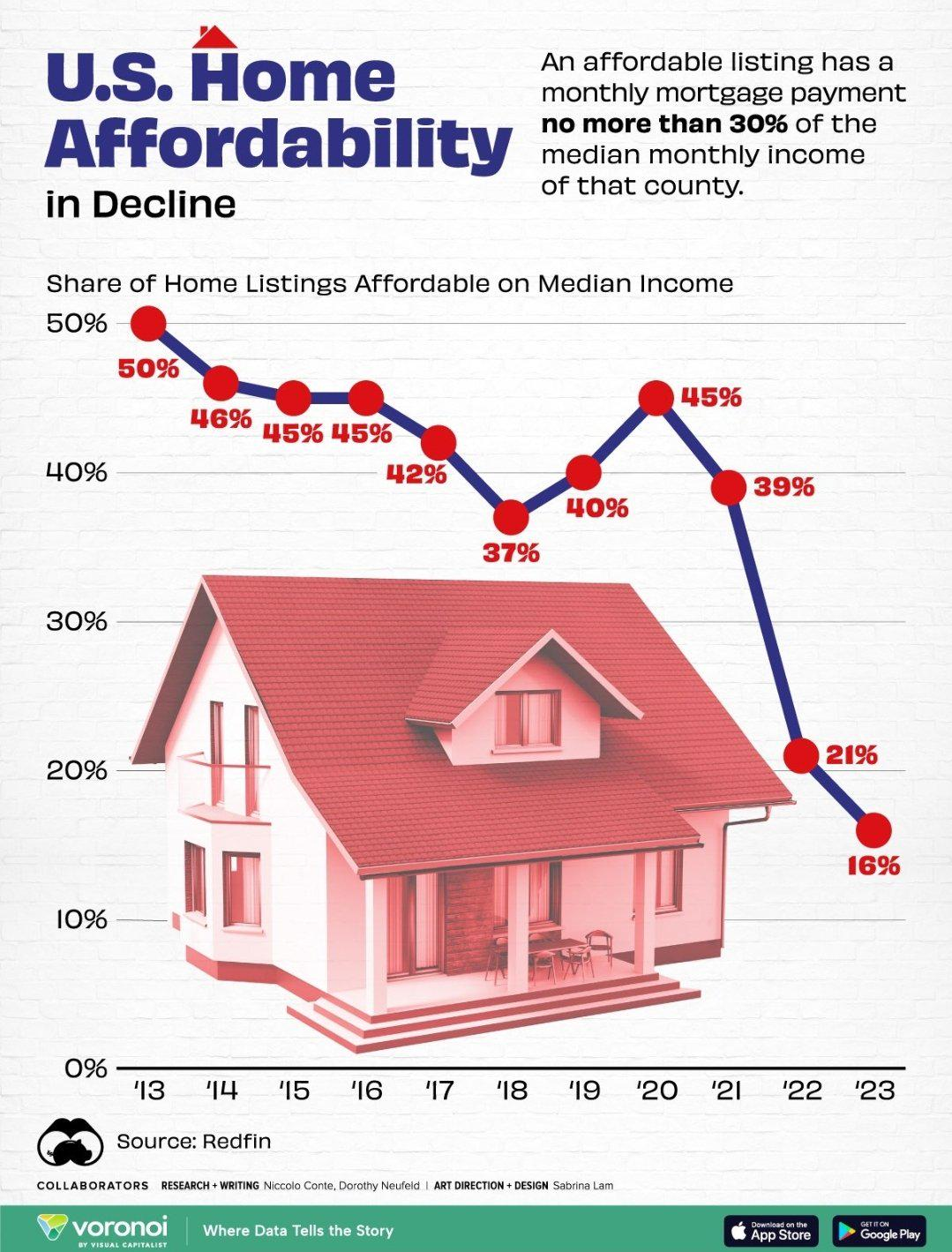
Understanding the Housing Affordability Crisis
The housing affordability crisis in the United States has reached unprecedented levels, with millions of potential homeowners struggling to secure a place to live. As the average price of single-family homes continues to skyrocket, many citizens find themselves priced out of the market, leading to increased demand for affordable housing solutions. This crisis not only affects individuals and families but also has broader implications for the economy, as homeownership is often seen as a key indicator of financial stability and community growth.
Factors contributing to this crisis include rising labor and material costs, and importantly, restrictive land-use regulations that severely limit construction opportunities. These regulations often arise from NIMBY sentiments, where existing homeowners resist new developments in their neighborhoods, fearing changes that could alter their community’s characteristics. As a result, the housing market faces significant challenges in meeting the demand for affordable options, perpetuating the cycle of unaffordability.
The Impact of Land-Use Regulations on Construction Productivity
Land-use regulations play a pivotal role in shaping the construction landscape in the United States. They set the parameters within which homes can be built, often leading to smaller projects that lack the economies of scale needed to reduce costs. Current studies suggest that tighter regulations restrict not only the size of housing developments but also the potential for builders to innovate. By requiring compliance with an intricate web of local zoning laws and planning approvals, builders are frequently forced into a more tedious and costly construction process.
As firms are limited in their ability to undertake large-scale projects, overall construction productivity declines. Research indicates that builders who operate at a larger scale can produce significantly more housing units per employee — a crucial factor, particularly when looking to address the housing affordability crisis. This decline in productivity contrasts sharply with the growth seen in other sectors, highlighting the unique challenges faced by the construction industry due to regulatory constraints.
NIMBY Policies: A Barrier to Homeownership
NIMBY (Not In My Backyard) policies have emerged as a significant barrier to constructing new housing, effectively impeding access to homeownership for many. The resistance from residents against new developments stems from various concerns, including the potential for increased traffic, changes in neighborhood aesthetics, and a perceived decline in property values. While these concerns are understandable, they often overshadow the pressing need for more housing, thereby exacerbating the crisis.
The ramifications of NIMBYism extend beyond individual neighborhoods, as cities struggle to accommodate the growing population. By limiting the options available for new housing, NIMBY policies disproportionately impact lower-income families seeking affordable homeownership opportunities. Consequently, as the supply of homes diminishes, prices continue to climb, solidifying a cycle of inequality in access to housing.
Challenges to Innovation in the Housing Market
Innovation in the housing market has become stagnant since the rise of stringent land-use regulations and NIMBY policies. Examining the data reveals a significant drop in patenting activity within the construction sector compared to other industries since the 1970s. The inability to innovate is directly linked to the constraints imposed by local regulations, which hinder builders from adopting new technologies or construction methods that could lower costs and enhance productivity.
As builders face increased scrutiny and additional hurdles in pursuing innovative designs, the quality and affordability of new homes continue to decline. This stagnation is particularly alarming in light of the burgeoning demand for efficient and sustainable housing solutions in the 21st century. To resolve these challenges, a reevaluation of land-use regulations and NIMBY policies is essential to foster a more conducive environment for innovation within the housing market.
The Economic Consequences of Stagnation in Homebuilding
The prolonged stagnation in the homebuilding sector signifies more than just a housing crisis; it poses serious economic ramifications for the broader U.S. economy. With fewer homes being constructed, there are fewer job opportunities in construction, leading to a ripple effect on related industries such as manufacturing and retail. As these sectors shrink, the overall economic growth of communities can stagnate, reinforcing cycles of poverty and diminishing the quality of life for many.
Additionally, the declining trend in homeownership undermines wealth accumulation for younger generations. The intergenerational transfer of housing wealth has shifted dramatically, with younger earners today holding significantly less equity in homes compared to their predecessors. This decline not only exacerbates social inequalities but also threatens the future economic stability of the nation, as homeownership has traditionally played a fundamental role in building wealth and fostering community development.
The Role of Construction Firms in Addressing the Housing Shortage
Construction firms have a critical role to play in alleviating the housing shortage and countering the affordability crisis. By adopting more efficient and scalable construction methods, companies can meet the growing demand for affordable housing while simultaneously increasing their market competitiveness. However, the current trend towards smaller construction firms, largely a consequence of regulatory burdens and NIMBY policies, has limited the potential for mass construction and innovation in housing.
To effectively address these challenges, larger construction firms must engage with local communities to navigate the regulatory landscape and advocate for changes that promote development. By fostering collaboration with government entities and community stakeholders, builders can pave the way for more sustainable and affordable housing solutions that meet the diverse needs of the population.
Leveraging Technology to Enhance Housing Production
Technology has the potential to revolutionize the housing production process, enabling builders to increase efficiency and reduce costs. Innovations such as prefabrication, modular construction, and advanced building materials not only improve productivity but also offer sustainable alternatives to traditional methods. However, to fully capitalize on these technological advancements, the industry must first address the regulatory barriers that currently impede their widespread adoption.
The integration of technology into the housing market could lead to significant reductions in construction times and costs, making homeownership more accessible for many. Furthermore, embracing engineering innovations can help to build stronger, more resilient structures that stand the test of time while meeting modern environmental standards. To achieve these benefits, builders and stakeholders in the housing sector must advocate for a legislative environment conducive to technological progress.
Future Directions for Housing Policy Reform
Amidst the growing housing affordability crisis, there is an urgent need for comprehensive housing policy reform. Policymakers must prioritize the examination and adjustment of land-use regulations that have historically stifled housing development. By fostering an environment that encourages rather than discourages new construction, communities can work towards alleviating housing shortages and promoting equitable access to homeownership.
Future reforms should also consider incentivizing builders to invest in large-scale projects that cater to diverse populations. Initiatives that promote community cooperation and stakeholder engagement can mitigate NIMBY sentiments while fostering inclusive planning and development practices. Ultimately, a multi-faceted approach to housing policy reform is crucial for overcoming the barriers to homeownership and stimulating economic growth.
The Importance of Community Engagement in Housing Development
Community engagement plays a vital role in the successful development of housing projects, particularly in navigating the complex landscape of land-use regulations and NIMBY attitudes. Builders and local governments must prioritize open communication with residents to address their concerns and expectations directly. By doing so, developers can cultivate trust and gain support for new construction projects, facilitating the planning process and enhancing community relationships.
Engagement strategies may include public forums, workshops, and collaborative planning sessions that involve residents in the decision-making process. Such initiatives empower communities to voice their opinions while allowing builders to incorporate valuable feedback into their project designs. Ultimately, fostering a culture of collaboration and transparency will help bridge the gap between developers and community members, leading to better housing outcomes.
Frequently Asked Questions
What role do land-use regulations play in the housing affordability crisis?
Land-use regulations significantly contribute to the housing affordability crisis by restricting the size of construction projects. These regulations often stem from NIMBY (Not In My Back Yard) policies that limit new developments, thereby reducing the availability of homes. By stifling large-scale projects, these regulations hinder mass production in the housing market, leading to increased costs and limited options for homeownership.
How do NIMBY policies affect the housing market and construction productivity?
NIMBY policies adversely affect the housing market by limiting the development of large-scale construction projects. As a result, smaller firms dominate the market, which leads to decreased construction productivity. This decline in productivity contributes to the rising costs of housing, exacerbating the housing affordability crisis and making homeownership less attainable for many Americans.
Can increasing construction productivity help mitigate the housing affordability crisis?
Yes, increasing construction productivity can significantly help mitigate the housing affordability crisis. By fostering a construction environment that allows for larger projects and mass-produced homes, costs can decrease, making homeownership more accessible. Addressing land-use regulations and NIMBY policies is crucial for enhancing construction productivity and thus improving housing affordability.
What impact do small housing developments have on homeownership rates?
Small housing developments typically result in fewer overall units being built, which constrains supply in the housing market. This limited supply, combined with high demand, drives prices up and diminishes homeownership rates. The housing affordability crisis is intensified by the prevalence of these smaller projects, particularly in areas with strict NIMBY regulations.
How does the historical decline in construction productivity relate to the current housing affordability crisis?
The historical decline in construction productivity, particularly since the 1970s, is closely tied to the current housing affordability crisis. As land-use regulations tightened, productivity fell dramatically, limiting the ability of builders to efficiently produce homes. This inefficiency contributes to higher housing costs and exacerbates the challenges faced by potential homeowners seeking affordable housing.
What solutions exist to address the housing affordability crisis linked to land-use regulation?
To address the housing affordability crisis linked to land-use regulation, potential solutions include reforming zoning laws to allow for more flexible building practices, reducing the restrictions imposed by NIMBY policies, and encouraging larger scale construction projects. By enhancing construction productivity and expanding housing supply, we can work towards making homeownership more achievable for a broader segment of the population.
Why is construction innovation important for solving the housing affordability crisis?
Construction innovation is vital for solving the housing affordability crisis because it can lead to more efficient building processes, reduced costs, and increased output. Innovating in construction methods and embracing technologies can help surpass the limitations imposed by existing land-use regulations and improve productivity, ultimately resulting in more affordable housing options for Americans.
How does the housing market’s response to land-use regulations affect economic growth?
The housing market’s response to land-use regulations directly affects economic growth by limiting the supply of affordable housing, which can stifle overall economic productivity. When housing becomes less affordable, it restricts the mobility of the workforce and diminishes consumer spending, leading to a slowdown in economic growth. Addressing these regulatory barriers is essential for fostering a more robust and dynamic economy.
| Key Point | Details |
|---|---|
| U.S. Housing Affordability Crisis | Homeownership is becoming increasingly unattainable, with prices for new single-family homes doubling since 1960. |
| Impact of Land-Use Policies | Restrictive land-use regulations, commonly known as NIMBY policies, are stifling builder productivity and innovation, leading to higher housing costs. |
| Fall in Construction Productivity | Between 1970 and 2000, productivity in the construction sector declined by 40%, as observed in the decrease of housing starts per worker. |
| Size of Construction Projects | The share of single-family homes being built in large-scale projects has fallen over a third, from previous levels where builders developed thousands of homes at once. |
| Innovation Decline in Housing Construction | Patent activity in construction has significantly lagged behind other industries since 1970, contributing to rising costs and stagnating production. |
| Demographic Housing Wealth Transfer | Younger generations are experiencing a substantial decline in housing wealth relative to older generations, exacerbating economic inequality. |
| Conclusion | |
Summary
The housing affordability crisis is a pressing issue that continues to escalate in the United States, primarily fueled by restrictive land-use regulations that hinder large-scale construction and innovation within the industry. As home prices rise and the availability of affordable housing diminishes, it is vital to explore solutions that can revitalize productivity in construction to reverse this troubling trend. By addressing these barriers to development, we can work towards a future where homeownership becomes attainable for all Americans.