The AI labor market is rapidly evolving, reshaping traditional employment landscapes and raising critical questions about the future of work. With artificial intelligence’s impact becoming increasingly pronounced, researchers are exploring job market trends that reveal significant occupational churn, particularly in technology-driven sectors. As businesses adapt to this economic disruption, the necessity for a skilled workforce capable of navigating new technologies has never been more urgent. This shift is not merely a trend but a pivotal moment that could determine the long-term trajectories of various professions. By examining how technology integrates into the workforce, we can better understand the profound implications for workers at all levels.
As we delve into the dynamics of the workforce influenced by advanced computing technologies, it’s crucial to assess the profound transformations underway. The contemporary job market is witnessing an influx of innovative solutions that fundamentally alter employment patterns, often referred to as the fourth industrial revolution. This digital evolution encourages ongoing occupational shifts and redefines the skill sets required in many professions. With terms like automation, robotic process automation, and digital transformation entering the conversation, stakeholders across industries must stay vigilant to navigate these changes effectively. Increasingly, the interplay between advanced technologies and human roles highlights the need for continuous adaptation and strategic foresight.
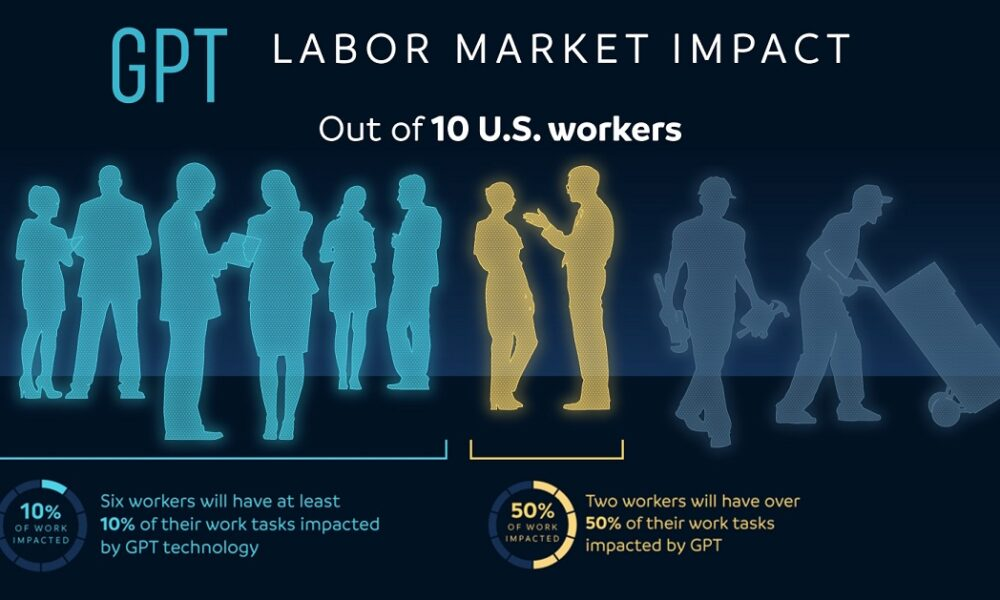
The Influence of AI on Job Market Trends
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is becoming a game-changer in shaping job market trends, fundamentally altering the way companies operate and how workers engage with their tasks. As outlined in the recent study by David Deming and Lawrence H. Summers, the infusion of AI technologies into various sectors has led to a notable increase in high-paying, specialized roles, particularly in fields related to science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM). This shift indicates a departure from traditional job polarization, where middle-income jobs have stagnated. Instead, organizations are now prioritizing highly trained professionals, reflecting a significant evolution in workforce demands driven by technological innovation.
Moreover, the emergence of AI technologies has not only influenced job creation but has also catalyzed occupational churn within the labor market. The historical analysis revealing trends in employment patterns underscores a structural transformation in the way jobs are structured and the skill sets required. Companies that harness AI effectively are noting higher operational efficiency and productivity, leading to an increased emphasis on hiring talent that possesses both technical knowledge and adaptability to emerging technologies. Consequently, this shift suggests that workers across various sectors must now adapt and upskill to remain competitive in a rapidly evolving job environment.
Understanding Occupational Churn Amidst Economic Disruption
Occupational churn refers to the shifting dynamics of job markets as certain roles become obsolete while new ones emerge. Historically, the U.S. labor market has experienced periods of volatility, particularly in response to significant technological advancements. The recent findings from Deming and Summers reveal that while the past decades saw a relatively stable job market, the last few years have been punctuated by significant changes driven by economic disruption, changes which are further accelerated by AI technology. This period of flux calls for a deeper understanding of how various factors contribute to job creation and destruction, necessitating an adaptive workforce.
The concept of economic disruption is crucial in analyzing the challenges workers face today. With rising automation and technological capabilities reshaping traditional roles, many low-paid service sector jobs are vanishing, reflecting a troubling trend for middle-to-low-income workers. The importance of equipping the workforce with relevant skills cannot be overstated; organizations that recognize and respond to these shifts will enhance their resilience in turbulent economic times. By investing in training and development, both employees and employers can foster a more flexible job market that is better prepared for ongoing disruption.
The Role of Technology in Workforce Transformation
The integration of advanced technologies such as AI is transforming the workforce in unprecedented ways. This relationship between technology and labor has been underscored by historical analysis showing that every major technological advancement has led to shifts in employment patterns. With AI at the forefront, there is clear evidence of an increasing demand for roles that require higher skill levels, particularly in areas such as data analysis and software development. The upsurge in technology deployment in business processes means that organizations are placing a premium on technical talent, which is reshaping career trajectories and skills required across industries.
Furthermore, the ongoing adaptation to these technological trends implies significant changes in how businesses will approach hiring and training. Employers now seek candidates not just with traditional qualifications but with a robust understanding of how to leverage technology in practical scenarios. This trend not only highlights the necessity for educational institutions to align their curriculums with industry demands but also emphasizes the need for ongoing professional development, ensuring that workers remain equipped to navigate this technological landscape.
Economic Implications of AI on Employment
The economic implications of AI on employment extend far beyond immediate job displacement. AI is positioned to drive productivity and profitability, but it also raises questions about the future of work and the types of jobs that will thrive in this new era. As businesses increasingly incorporate AI into their operations, there is a notable shift towards roles that require specialized skills—particularly in the technology sector, where the growth of STEM roles has become pronounced. This trend mirrors broader labor market trends where higher-skilled positions are becoming more desirable, while the demand for low-skilled labor continues to decline.
However, this technological advancement is not without its challenges. As companies prioritize efficiency and cost-cutting through automation, many low-paid service jobs are witnessing stagnation or decline. The economic landscape becomes more complex as workers in these roles face significant hurdles in transitioning to new employment opportunities. Policymakers must consider how these changes will affect overall economic health, wage distributions, and the safety nets in place to support displaced workers as they navigate the challenges posed by a rapidly evolving labor market.
Navigating Automation Anxiety in the Workforce
Automation anxiety has emerged as a significant concern among workers facing the prospect of job displacement due to AI and robotics. Historically, periods of intense technological change have led to job insecurity and fears about the future of work, echoing sentiments felt during past economic disruptions. Deming’s research illustrates that while automation had previously stagnated job growth in certain areas, the onset of AI has re-ignited these concerns by introducing new ways that machines can outpace human capabilities in various tasks.
To combat automation anxiety, it is essential for organizations to foster a culture of innovation and continuous learning among employees. Developing strategies that emphasize re-skilling and up-skilling can help workers to embrace technological change rather than fear it. By providing support for lifelong learning and adaptability, both workers and organizations can navigate the uncertainties of automation more effectively and thrive in an environment where AI is an integral partner in the workforce.
Embracing Continuous Learning in the Age of AI
In a labor market increasingly influenced by technological advancement, embracing continuous learning is paramount for all workers. The study by Deming and Summers poignantly highlights the need for individuals to be proactive in developing their skills, particularly in technology-driven fields where demands evolve rapidly. Continuous education programs and initiatives that focus on AI competency can empower workers, equipping them to adapt to new roles that emerge as AI reshapes job responsibilities and functions.
Moreover, organizations that support a culture of learning will not only enhance their competitive edge but also foster employee loyalty and job satisfaction. By investing in training programs for their workforce, companies can bridge the skills gap and ensure that talent aligns with the needs of a technology-centric market. As roles transform and new opportunities arise, fostering a mindset of continuous improvement can lead to not only personal growth for employees but also organizational resilience in an ever-changing economic landscape.
AI’s Transformative Impact on Knowledge Workers
The implications of AI are particularly pronounced for knowledge workers, who have traditionally relied on their expertise in fields such as finance, management, and journalism. As AI technologies become more integrated into everyday tasks, there is a growing concern about how these advancements will affect the nature of work performed in these sectors. The historical perspective offered by Deming and Summers sheds light on past occupational shifts, illustrating that while automation may enhance productivity, the reliance on technology poses risks of displacement.
It is crucial for knowledge workers to evolve alongside these changes by enhancing their technical skills and digital literacy. As clients and employers demand quicker results and more adept utilization of technology, knowledge workers must be prepared to leverage AI as a tool for productivity rather than viewing it strictly as competition. This transformation requires the workforce to redefine their roles in an increasingly automated context, moving towards positions that complement technological capabilities while providing added value through human insight and creativity.
Future Job Opportunities in Emerging Technologies
As AI continues to reshape the labor market landscape, new job opportunities are emerging within the framework of the digital economy. The increase in STEM-related jobs reflects a significant shift towards technical fields that are set to dominate future employment trends. With sectors like data science, machine learning, and AI development on the rise, these roles are characterized by higher compensation and demand for specialized skills. This presents a unique opportunity for workers to position themselves strategically within the job market.
Additionally, the evolution of e-commerce and technology-driven sectors necessitates a workforce adept in emerging technologies. As businesses embrace new paradigms for engaging consumers and optimizing operations through data-driven insights, the need for skilled professionals who can navigate and harness these technologies effectively is paramount. Workers who invest in learning these in-demand skills will not only increase their job security but will also contribute to the overarching evolution of the job market as we transition into more tech-centric economies.
Preparing for the Future: Skills for the AI-Driven Economy
Looking ahead, preparing for the AI-driven economy requires a robust understanding of the skills that will be in demand. As companies seek to integrate AI into their operations, those who possess a blend of technical expertise and critical thinking will stand out in the job market. Emphasizing the importance of adaptability, workers are encouraged to engage in skills development that focuses on data analysis, programming, and machine learning—areas that are increasingly relevant in various contexts across sectors.
Moreover, fostering soft skills such as communication, problem-solving, and creativity will complement technical abilities, creating a well-rounded workforce equipped to tackle the challenges posed by automation. Educational institutions and employers must collaboratively promote programs that not only prioritize hard skills associated with technology but also encourage the development of interpersonal capabilities. By preparing for the shifting landscape of work, both individuals and organizations can ensure they remain competitive and relevant in an economy where AI plays a pivotal role.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is the AI labor market impacting job market trends in the U.S.?
The AI labor market is significantly influencing job market trends in the U.S. by driving a surge in STEM-related employment, decreasing low-paid service jobs, and reducing the share of retail sales jobs. AI’s integration into various sectors is reshaping the workforce, leading to a demand for high-skilled positions while at the same time contributing to occupational churn.
What trends are emerging from the research on artificial intelligence’s impact on the labor market?
Research on artificial intelligence’s impact on the labor market reveals four key trends: a shift towards high-paying jobs requiring advanced skills, an increase in STEM job offerings, a decline in low-paid service sector jobs, and a notable reduction in retail sales positions due to technology adoption. These trends highlight AI’s transformative role in shaping employment opportunities.
How does occupational churn relate to technology in the workforce?
Occupational churn relates to technology in the workforce as it illustrates how technological advancements—including AI—affect job stability and employment patterns. The study of over 100 years of data indicates that significant disruptions coincided with the introduction of breakthrough technologies, leading to shifts in job availability across various sectors.
What is ‘automation anxiety’ in the context of the AI labor market?
‘Automation anxiety’ refers to the fear that AI and automation technologies will replace significant portions of jobs. This concern peaked in the early 2000s, with studies suggesting that nearly half of U.S. occupations faced risks from computerization. Recent findings indicate a resurgence in AI’s influence, raising new questions about job security and the future of work.
Are there long-term risks associated with AI-related economic disruption?
Yes, while AI presents opportunities for productivity gains, there are long-term risks associated with economic disruption. As companies seek efficiency, they may increasingly demand higher performance from workers, potentially leading to job displacement for those unable to adapt to the evolving AI landscape.
What role does investment in AI play in shaping the labor market?
Investment in AI plays a crucial role in shaping the labor market by fostering growth in technical jobs and revolutionizing traditional employment sectors. As companies allocate resources toward AI technologies, they not only create new job opportunities but also necessitate a workforce skilled in using these advancements effectively.
How does AI affect the future of low-paid service jobs?
AI is expected to negatively impact the future of low-paid service jobs. The study identified a decline in employment in these sectors as companies increasingly turn to automated solutions for tasks previously performed by humans, suggesting a need for workers to adapt to shifting job requirements and focus on higher-skilled roles.
What can workers in various industries expect from the AI labor market?
Workers across various industries should anticipate a changing landscape due to the AI labor market. While some may find new opportunities in emerging fields, others may need to enhance their skills to remain competitive as AI transforms job functions and organizational demands.
How has the COVID-19 pandemic accelerated changes in the AI labor market?
The COVID-19 pandemic has accelerated changes in the AI labor market by hastening the adoption of e-commerce and online services. It has shifted consumer behaviors, forcing businesses to innovate and utilize AI solutions, thereby impacting job availability and requirements in traditional retail and service sectors.
| Trend | Description |
|---|---|
| Decline of Job Polarization | Shift in labor market favoring high-compensated, skilled employees, with less focus on low-paid jobs. |
| Surge in STEM Jobs | Notable increase in STEM roles, with jobs like software developers rising from 6.5% to nearly 10% of the market from 2010 to 2024. |
| Stagnation in Low-Paid Service Jobs | Significant decline in employment in low-paid service sectors since 2019, attributed partially to AI. |
| Drop in Retail Sales Jobs | Reduction of retail sales jobs from 7.5% to 5.7% of the labor market due to technology and the rise of e-commerce. |
| Workplace Displacement Risks | AI may boost productivity in the short term but poses risks of worker displacement in the long term. |
Summary
The AI labor market is currently undergoing significant transformations as evidenced by a recent study from Harvard economists. With trends like the decline of job polarization and a surge in STEM positions, it’s clear that AI is reshaping the employment landscape. The findings indicate that while certain low-paid jobs are declining, opportunities for skilled workers are on the rise. As companies heavily invest in AI, understanding these dynamics becomes essential for workers across all sectors to navigate the evolving job market effectively.